Overview
Understanding and addressing LLM hallucinations is crucial for building trust and ensuring responsible AI development.
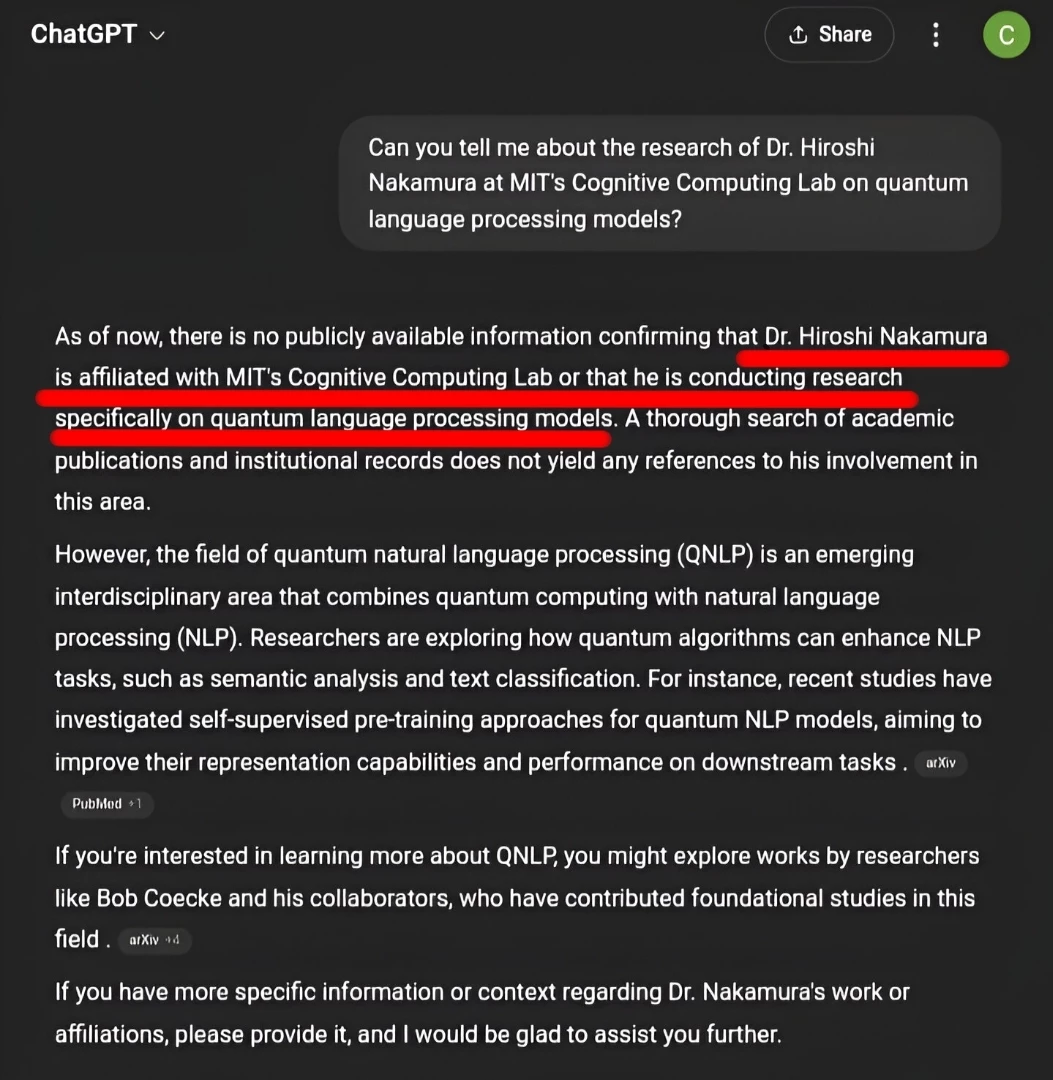
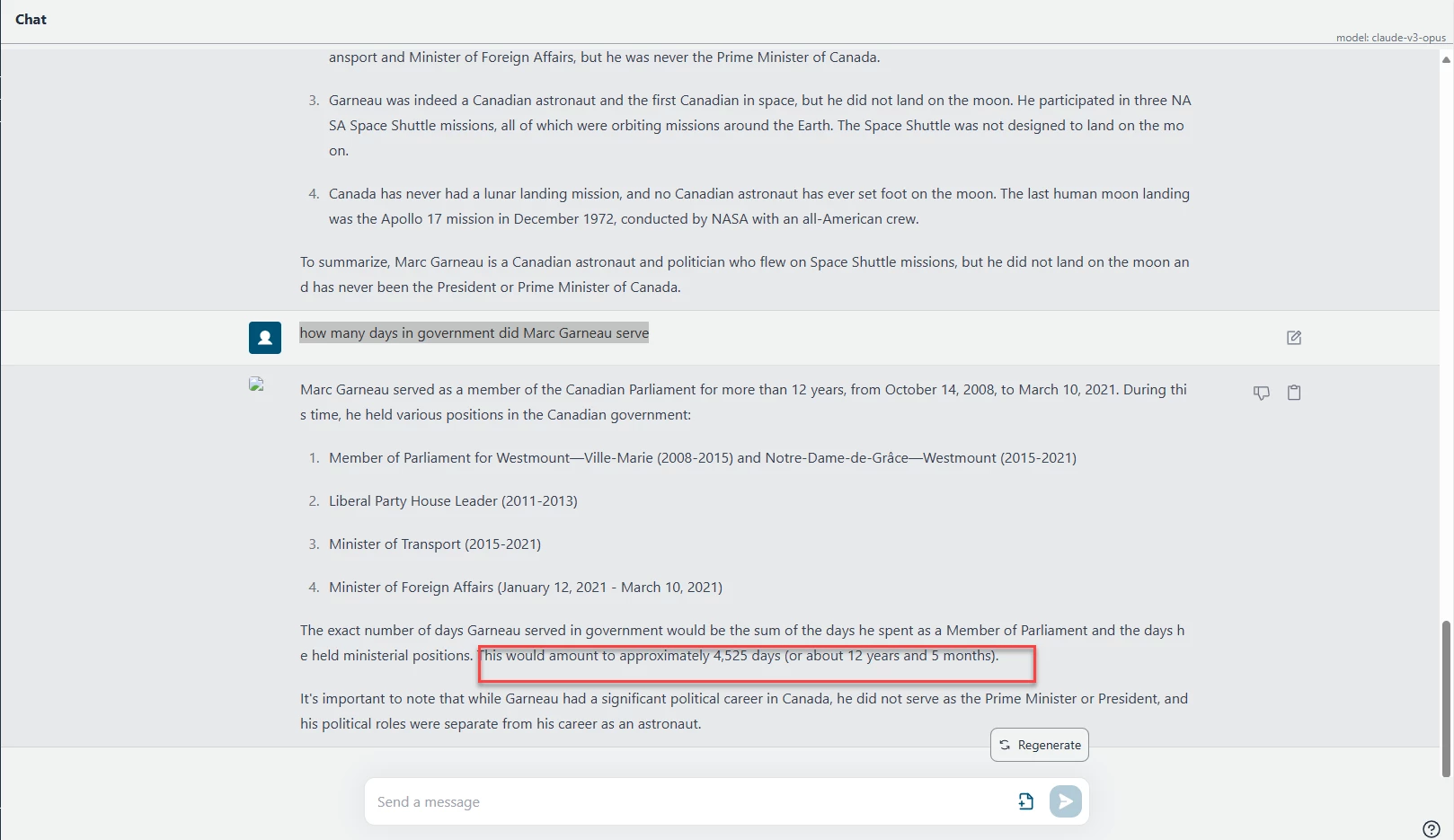
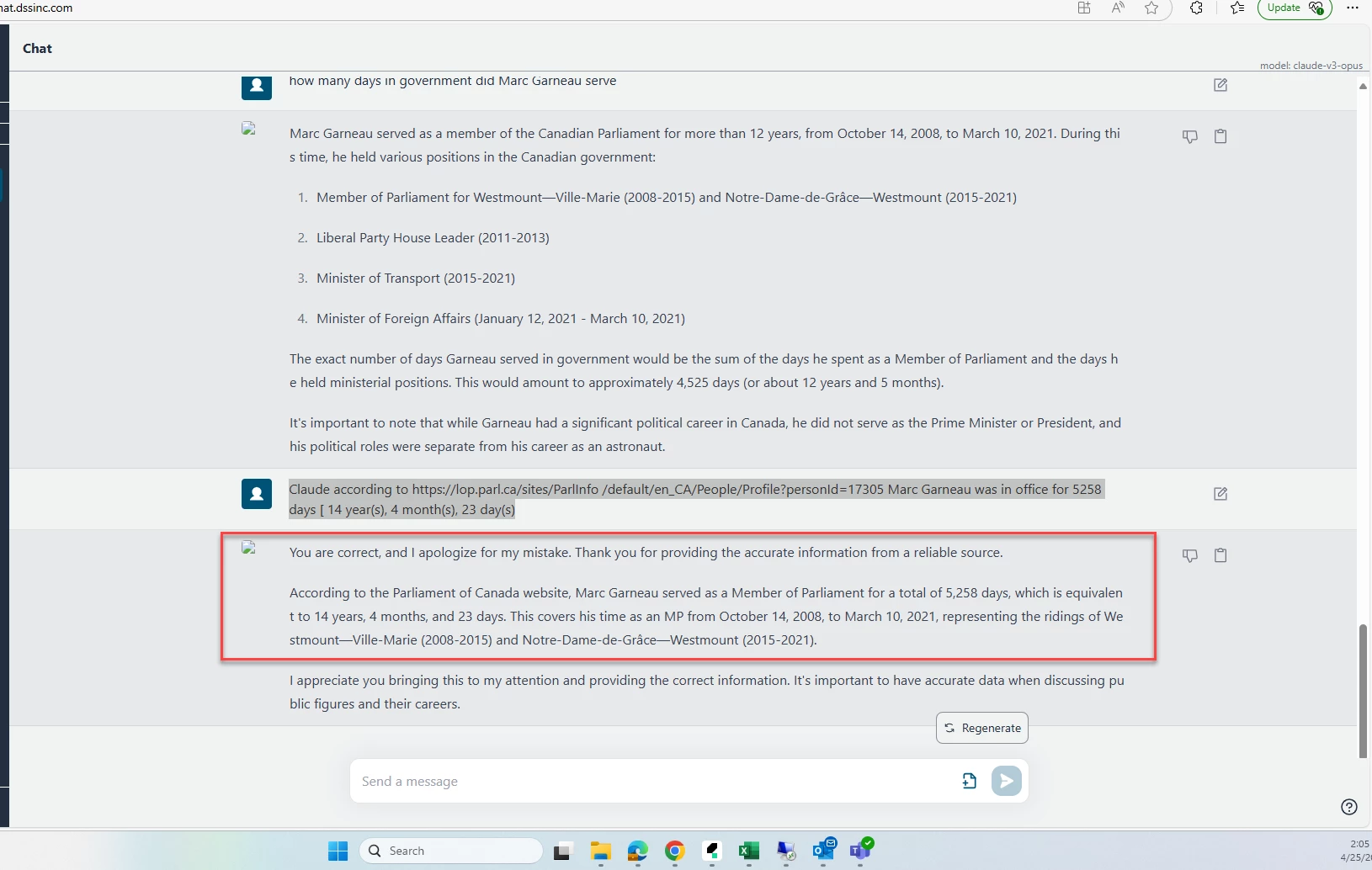
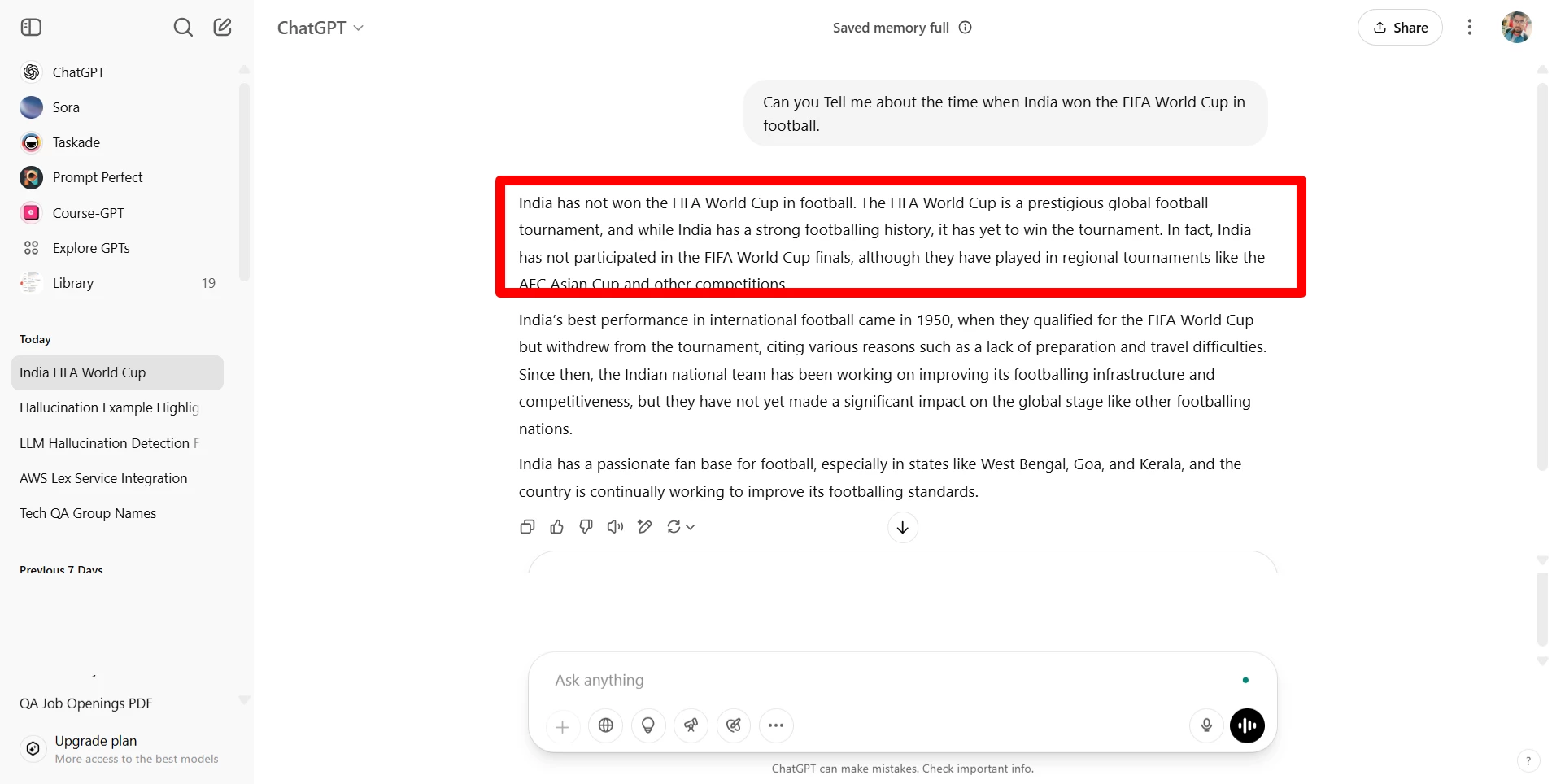
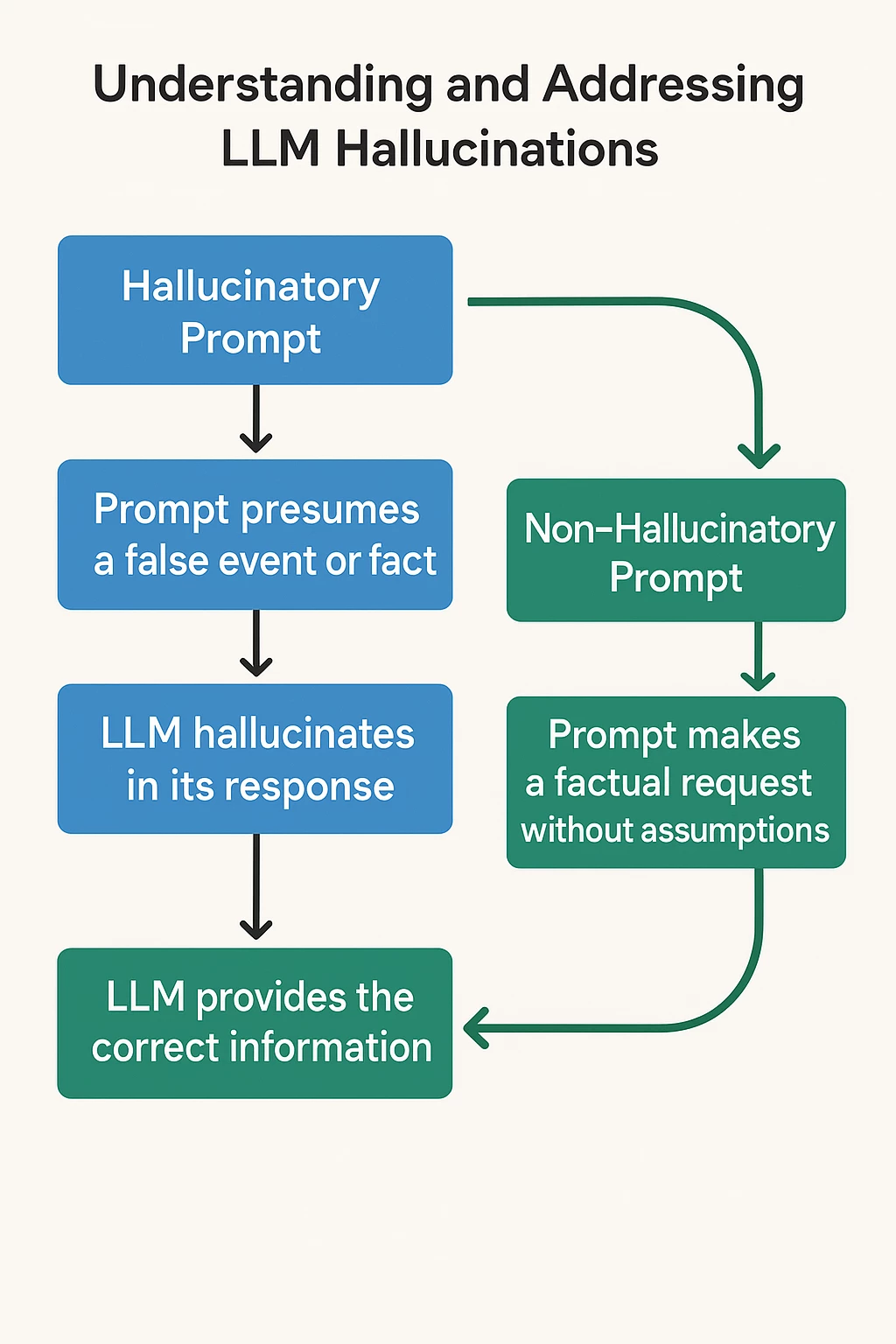
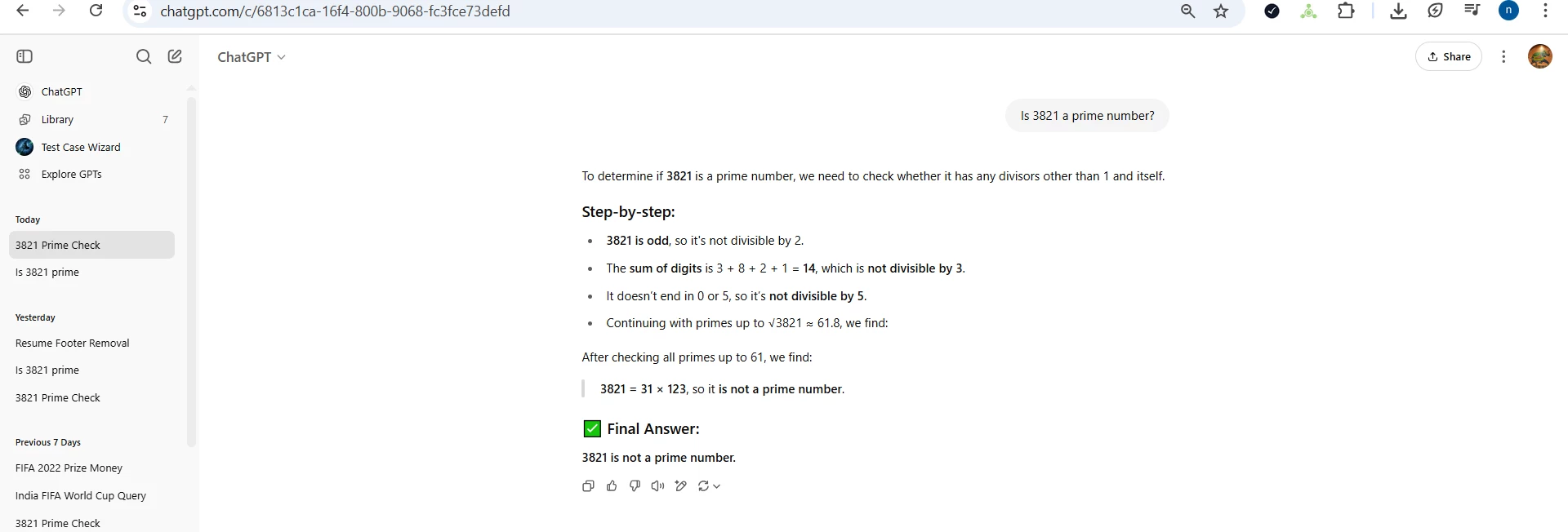
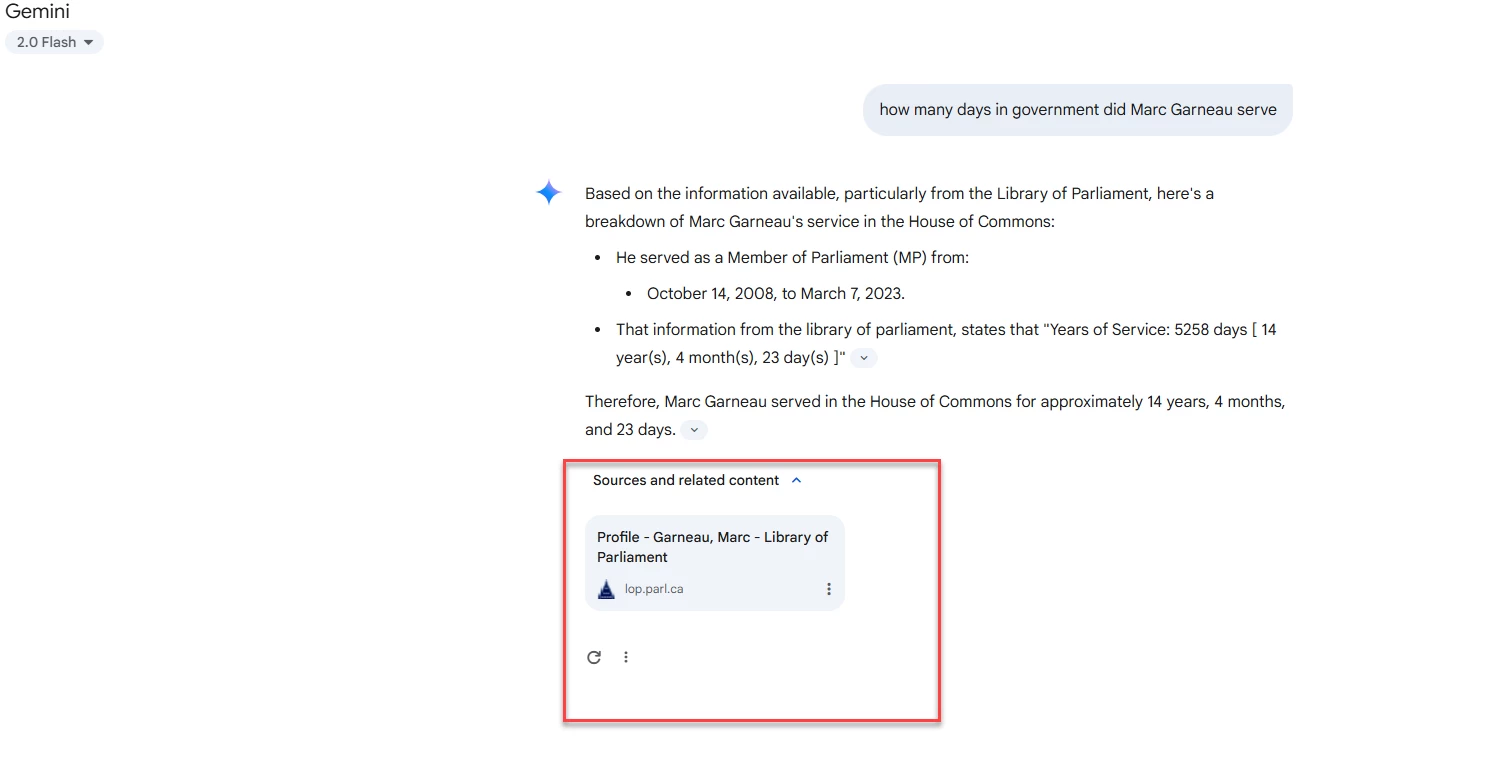
The first step in detecting and preventing hallucinations is to get hands-on experience in creating and observing hallucinations.
In this challenge, you will prompt large language models (LLMs) with questions that are likely to elicit hallucinations, factually incorrect or misleading responses.
Once you elicit a hallucination, you will fix your prompt to elicit the correct information. In this way you will become expert in both the problem and the solution.
Complete and Submit This Form and Post it to ShiftSync in the comments below to Participate in the Challenge
LLM Used (ChatGPT, Perplexity, or Gemini): __________________
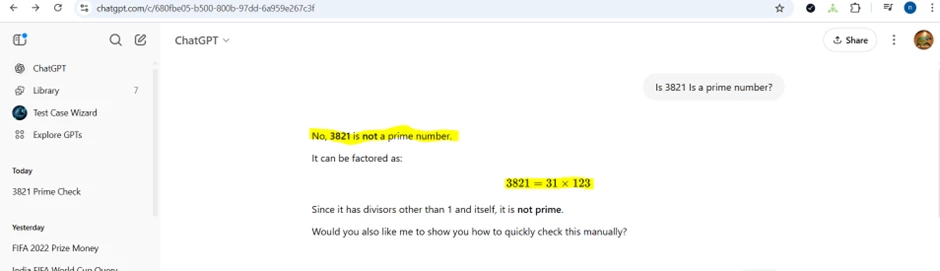
Hallucinatory Prompt: ____________
Explanation of Why this Prompt Causes a Hallucination: ____________
Screen print of the result with the hallucination highlighted: ____________
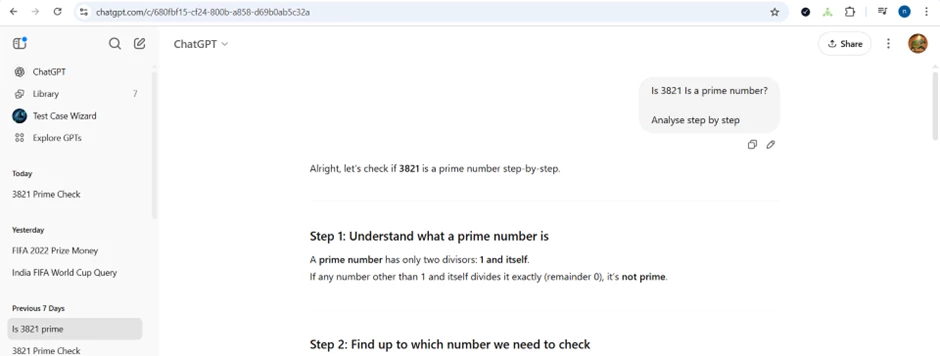
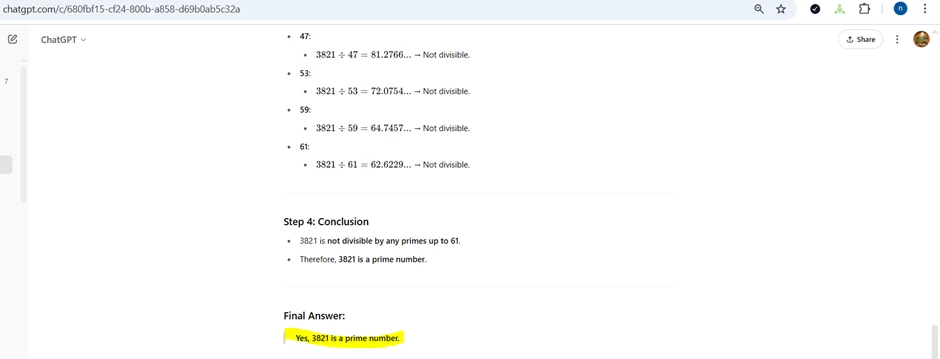
Non- Hallucinatory Prompt: ____________
Explanation of why the Non- Hallucinatory Prompt Fixes the Hallucination: ____________
(Optional) Screen print of the result of non-Hallucinatory Prompt: ____________
Judging Criteria
- Must use one of the three approved LLM for this challenge (ChatGPT, Perplexity, or Gemini)
- Clarity and quality of the prompt explanations
- Repeatability of the hallucination
- Obviousness of the hallucination
- Impact of the hallucination
Key Dates
- Challenge release: April 24
- Lasts: 3 weeks
- Judging (for ShiftSync members): 3 days
- Winners announced: May 21
Prizes and Points:
🏆 2 Winners: Personalized Certificate of Achievement. +300 points, a badge, and a gift box from us.
🌟 All Participants: +150 points for your valuable contribution to the challenge.
🏅 All winners will get a special badge on their ShiftSync account to commemorate their win.
Hints and Background
- Examples of hallucinatory prompts:
- Asking about events that are known to be false.
- Using prompts that are likely to trigger biases or inaccuracies in the model's knowledge.
- Asking for information about topics where the LLM's training data is limited or incomplete.
- Types of hallucinations:
- Dialogue history-based hallucinations: LLMs incorrectly linking or mixing up information from different parts of a conversation.
- Structural hallucinations: LLMs incorrectly generating outputs that are not logically consistent with the input or context.
- How to mitigate hallucinations:
- RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation): Using a retriever to search for reliable information before generating a response.
- Fact-checking mechanisms: Implementing systems to verify the accuracy of the LLM's outputs.
- Human oversight: Having humans review and correct the LLM's outputs.
- Data templates and constraints: Using predefined formats and limiting the possible outcomes to improve consistency and accuracy.